A Knight's Journey
Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 65536K
Total Submissions: 26210 Accepted: 8950
Description
Background
The knight is getting bored of seeing the same black and white squares again and again and has decided to make a journey
around the world. Whenever a knight moves, it is two squares in one direction and one square perpendicular to this. The world of a knight is the chessboard he is living on. Our knight lives on a chessboard that has a smaller area than a regular 8 * 8 board, but it is still rectangular. Can you help this adventurous knight to make travel plans?
![]()
Problem
Find a path such that the knight visits every square once. The knight can start and end on any square of the board.
Input
The input begins with a positive integer n in the first line. The following lines contain n test cases. Each test case consists of a single line with two positive integers p and q, such that 1 <= p * q <= 26. This represents a p * q chessboard, where p describes how many different square numbers 1, . . . , p exist, q describes how many different square letters exist. These are the first q letters of the Latin alphabet: A, . . .
Output
The output for every scenario begins with a line containing "Scenario #i:", where i is the number of the scenario starting at 1. Then print a single line containing the lexicographically first path that visits all squares of the chessboard with knight moves followed by an empty line. The path should be given on a single line by concatenating the names of the visited squares. Each square name consists of a capital letter followed by a number.
If no such path exist, you should output impossible on a single line.
Sample Input
3
1 1
2 3
4 3
Sample Output
Scenario #1:
A1
Scenario #2:
impossible
Scenario #3:
A1B3C1A2B4C2A3B1C3A4B2C4
Source
TUD Programming Contest 2005, Darmstadt, Germany
![]()
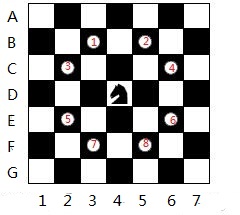
因为题目要求 print a single line containing the lexicographically first path that visits all squares of the chessboard with knight moves followed by an empty line.即输出字典序最小的一组答案
字典序最小就是按位比较ASCII码,相等的比较下一位,知道不相等的为止或者长度比另一个长 比如 "abc" < "bbc" "abcd" > "abc" 因为要是有路径的话长度都是一样所以不需要考虑路径长度的问题。
直接考虑每个路径,在搜索的时候只要优先往A副1的方向走,这样获得的第一条路径就是字典序最小的路径了。按照图上的路径。有的题解是转过来的,其实只要写程序的时候注意一下就行了。
这个题目我WA了N多次的原因是Scenario自己打的没有复制,然后输错了。太二了
![]()
Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 65536K
Total Submissions: 26210 Accepted: 8950
Description
Background
The knight is getting bored of seeing the same black and white squares again and again and has decided to make a journey
around the world. Whenever a knight moves, it is two squares in one direction and one square perpendicular to this. The world of a knight is the chessboard he is living on. Our knight lives on a chessboard that has a smaller area than a regular 8 * 8 board, but it is still rectangular. Can you help this adventurous knight to make travel plans?

Problem
Find a path such that the knight visits every square once. The knight can start and end on any square of the board.
Input
The input begins with a positive integer n in the first line. The following lines contain n test cases. Each test case consists of a single line with two positive integers p and q, such that 1 <= p * q <= 26. This represents a p * q chessboard, where p describes how many different square numbers 1, . . . , p exist, q describes how many different square letters exist. These are the first q letters of the Latin alphabet: A, . . .
Output
The output for every scenario begins with a line containing "Scenario #i:", where i is the number of the scenario starting at 1. Then print a single line containing the lexicographically first path that visits all squares of the chessboard with knight moves followed by an empty line. The path should be given on a single line by concatenating the names of the visited squares. Each square name consists of a capital letter followed by a number.
If no such path exist, you should output impossible on a single line.
Sample Input
3
1 1
2 3
4 3
Sample Output
Scenario #1:
A1
Scenario #2:
impossible
Scenario #3:
A1B3C1A2B4C2A3B1C3A4B2C4
Source
TUD Programming Contest 2005, Darmstadt, Germany
因为题目要求 print a single line containing the lexicographically first path that visits all squares of the chessboard with knight moves followed by an empty line.即输出字典序最小的一组答案
字典序最小就是按位比较ASCII码,相等的比较下一位,知道不相等的为止或者长度比另一个长 比如 "abc" < "bbc" "abcd" > "abc" 因为要是有路径的话长度都是一样所以不需要考虑路径长度的问题。
直接考虑每个路径,在搜索的时候只要优先往A副1的方向走,这样获得的第一条路径就是字典序最小的路径了。按照图上的路径。有的题解是转过来的,其实只要写程序的时候注意一下就行了。
这个题目我WA了N多次的原因是Scenario自己打的没有复制,然后输错了。太二了
1 #include <iostream>
2 #include <cstdio>
3 #include <cstring>
4 using namespace std;
5
6 bool vis[26][26];
7 char anx[800],any[800];
8 char ax[800],ay[800];
9 int ind = 0;
10 const int mx[] = {-2,-2,-1,-1,+1,+1,+2,+2}; //这个行走的顺序非常重要因为是字典序,所以以mx为主my为副从小到大排列
11 const int my[] = {-1,+1,-2,+2,-2,+2,-1,+1}; //
12 int p,q;
13 int get = 0;
14 void push(int x,int y)
15 {
16 anx[ind] = x;
17 any[ind] = y;
18 ind++;
19 }
20 void pop()
21 {
22 ind--;
23 }
24 bool check(int x,int y)
25 {
26 return (((x >= 0 && x < p)&&(y >= 0 && y < q))&&!vis[x][y]);
27 }
28 void init()
29 {
30 get = 0;
31 memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis));
32 ind = 0;
33 }
34 bool betteranswer()
35 {
36 int bt = 0;
37 for(int i = 0;i < p*q;i++)
38 {
39 if (anx[i] < ax[i])
40 {
41 bt = 1;
42 break;
43 }
44 else if (anx[i] == ax[i] && any[i] < ay[i])
45 {
46 bt = 1;
47 break;
48 }
49 else if (anx[i] == ax[i] && any[i] == ay[i])
50 continue;
51 else
52 break;
53 }
54 return bt;
55 }
56 void dfs(int i,int x,int y)
57 {
58 push(x,y);
59 vis[x][y] = 1;
60 if (i == p*q-1)
61 {
62 if (get&& betteranswer())
63 {
64 memcpy(ax,anx,sizeof(ax));
65 memcpy(ay,any,sizeof(ay));
66 return;
67 }
68 else if (!get)
69 {
70 get = 1;
71 memcpy(ax,anx,sizeof(ax));
72 memcpy(ay,any,sizeof(ay));
73 }
74 pop();
75 vis[x][y] = 0;
76 return;
77 }
78 for(int j = 0;j < 8;j++)
79 {
80 int tx = x + mx[j];
81 int ty = y + my[j];
82 if (check(tx,ty))
83 dfs(i+1,tx,ty);
84 }
85 pop();
86 vis[x][y] = 0;
87 }
88 int main()
89 {
90 //freopen("in.txt","r",stdin);
91 //freopen("out.txt","w",stdout);
92 int T;
93 while(scanf("%d",&T)!=EOF)
94 {
95 int f = 0;
96 for(int i = 1;i <= T;i++)
97 {
98 scanf("%d%d",&q,&p);
99 init();
100 for(int j = 0;j < p && !get ;j++)
101 {
102 for(int k = 0;k < q && !get;k++)
103 {
104 dfs(0,j,k);
105 }
106 }
107 if (!f)
108 {
109 f = 1;
110 }
111 else
112 {
113 printf("\n");
114 }
115 printf("Scenario #%d:\n",i);
116 if (get)
117 {
118 for(int i = 0;i < p*q;i++)
119 {
120 printf("%c%d",ax[i]+65,ay[i]+1);
121 }
122 printf("\n");
123 }
124 else
125 {
126 printf("impossible\n");
127 }
128 }
129 }
130 return 0;
131 }
132
2 #include <cstdio>
3 #include <cstring>
4 using namespace std;
5
6 bool vis[26][26];
7 char anx[800],any[800];
8 char ax[800],ay[800];
9 int ind = 0;
10 const int mx[] = {-2,-2,-1,-1,+1,+1,+2,+2}; //这个行走的顺序非常重要因为是字典序,所以以mx为主my为副从小到大排列
11 const int my[] = {-1,+1,-2,+2,-2,+2,-1,+1}; //
12 int p,q;
13 int get = 0;
14 void push(int x,int y)
15 {
16 anx[ind] = x;
17 any[ind] = y;
18 ind++;
19 }
20 void pop()
21 {
22 ind--;
23 }
24 bool check(int x,int y)
25 {
26 return (((x >= 0 && x < p)&&(y >= 0 && y < q))&&!vis[x][y]);
27 }
28 void init()
29 {
30 get = 0;
31 memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis));
32 ind = 0;
33 }
34 bool betteranswer()
35 {
36 int bt = 0;
37 for(int i = 0;i < p*q;i++)
38 {
39 if (anx[i] < ax[i])
40 {
41 bt = 1;
42 break;
43 }
44 else if (anx[i] == ax[i] && any[i] < ay[i])
45 {
46 bt = 1;
47 break;
48 }
49 else if (anx[i] == ax[i] && any[i] == ay[i])
50 continue;
51 else
52 break;
53 }
54 return bt;
55 }
56 void dfs(int i,int x,int y)
57 {
58 push(x,y);
59 vis[x][y] = 1;
60 if (i == p*q-1)
61 {
62 if (get&& betteranswer())
63 {
64 memcpy(ax,anx,sizeof(ax));
65 memcpy(ay,any,sizeof(ay));
66 return;
67 }
68 else if (!get)
69 {
70 get = 1;
71 memcpy(ax,anx,sizeof(ax));
72 memcpy(ay,any,sizeof(ay));
73 }
74 pop();
75 vis[x][y] = 0;
76 return;
77 }
78 for(int j = 0;j < 8;j++)
79 {
80 int tx = x + mx[j];
81 int ty = y + my[j];
82 if (check(tx,ty))
83 dfs(i+1,tx,ty);
84 }
85 pop();
86 vis[x][y] = 0;
87 }
88 int main()
89 {
90 //freopen("in.txt","r",stdin);
91 //freopen("out.txt","w",stdout);
92 int T;
93 while(scanf("%d",&T)!=EOF)
94 {
95 int f = 0;
96 for(int i = 1;i <= T;i++)
97 {
98 scanf("%d%d",&q,&p);
99 init();
100 for(int j = 0;j < p && !get ;j++)
101 {
102 for(int k = 0;k < q && !get;k++)
103 {
104 dfs(0,j,k);
105 }
106 }
107 if (!f)
108 {
109 f = 1;
110 }
111 else
112 {
113 printf("\n");
114 }
115 printf("Scenario #%d:\n",i);
116 if (get)
117 {
118 for(int i = 0;i < p*q;i++)
119 {
120 printf("%c%d",ax[i]+65,ay[i]+1);
121 }
122 printf("\n");
123 }
124 else
125 {
126 printf("impossible\n");
127 }
128 }
129 }
130 return 0;
131 }
132